
sudo apt full-upgradeīe extra careful when using this command.
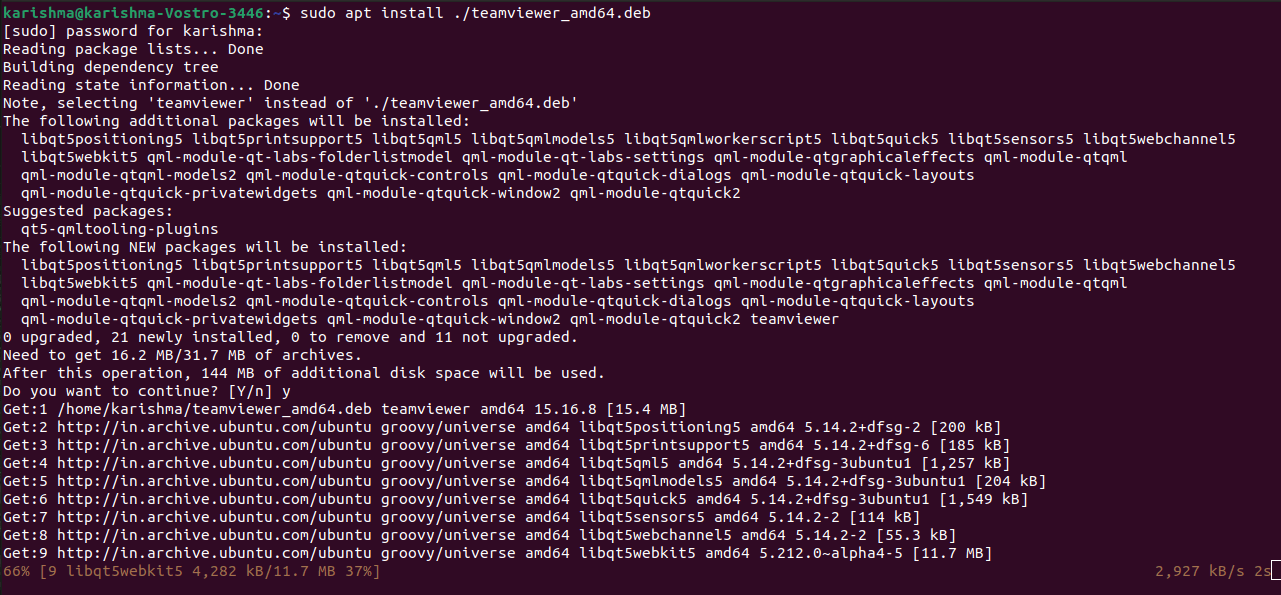
The difference between upgrade and full-upgrade is that the later will remove the installed packages if that is needed to upgrade the whole system. It is always a good idea to configure automatic security updates If you want to upgrade a single package, pass the package name: sudo apt upgrade package_name The command doesn’t upgrade packages that require removal of installed packages. To upgrade the installed packages to their latest versions run: sudo apt upgrade Regularly updating your Linux system is one of the most important aspects of overall system security. Upgrading packages ( apt upgrade) #Īpt Command in Linux: Examples for Ubuntu and Debian This will pull the latest changes from the APT repositories: sudo apt updateĪlways update the package index before upgrading or installing new packages. To update the package index run the command below. The APT package index is basically a database that holds records of available packages from the repositories enabled in your system. This guide serves as a quick reference for the apt commands. Most of the apt commands must be run as a user with sudo Prefer using apt-get and apt-cache in your shell scripts as they are backward compatible between the different versions and have more options and features.

It combines the most frequently used commands from the apt-get and apt-cache tools with different default values of some options.Īpt is designed for interactive use. Apt is a command-line utility for installing, updating, removing, and otherwise managing deb packages on Ubuntu, Debian, and related Linux distributions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
